Low Carb Diet Benefits – 7 Powerful Health Transformations Revealed

Table of Contents
So you’ve been hearing everyone talk about the low carb diet lately and you’re sitting there wondering if cutting carbs is actually gonna make a difference in your health, right? With all the conflicting information out there – some people swearing by carbohydrate restriction while others warn about potential dangers – it’s totally understandable if you feel confused about whether this eating approach is right for you.
Here’s the truth though – when done correctly with whole, nutrient-dense foods, a low carb diet can deliver some seriously impressive health benefits that go way beyond just losing a few pounds. We’re talking about real metabolic improvements, better blood sugar control, enhanced mental clarity, and reduced risk factors for chronic diseases that affect millions of people worldwide.
Whether you’re curious about the Atkins diet, interested in a low glycemic diet, or just want to understand what happens when you reduce your carbohydrate intake, this comprehensive guide breaks down seven science-backed benefits that make low carb eating worth considering for your health transformation journey.

Image Description: Professional hero image showing a beautifully arranged plate with low carb foods including grilled chicken, avocado, leafy greens, nuts, and colorful vegetables
Alt Text: low carb diet
Caption: Discover seven powerful low carb diet benefits backed by scientific research
What Exactly Is A Low Carb Diet And How Does It Work
Before we dive into the incredible benefits, lets get super clear on what we actually mean by a low carb diet and how it differs from the standard way most people eat today.
According to research from the National Institutes of Health, there’s no universal agreement on exactly what defines “low carb,” but most definitions involve restricting carbohydrate intake to somewhere between 20 to 130 grams per day – significantly lower than the typical Western diet that often includes 200 to 300 grams daily.
When you dramatically reduce your carb intake through carbohydrate restriction, your body undergoes some pretty remarkable metabolic shifts. Instead of relying primarily on glucose from carbs for energy, your body starts breaking down fat for fuel and producing ketone bodies – an alternative energy source that your brain and other tissues can use efficiently.
The Atkins diet, popularized decades ago, was one of the first mainstream low carb approaches that demonstrated significant weight loss and health improvements. Modern variations include ketogenic diets, paleo approaches, and low glycemic diet plans that focus on foods that don’t spike blood sugar levels dramatically.
Benefit One: Dramatic Appetite Reduction Without Constant Hunger
Lets be real – one of the absolute worst parts of traditional dieting is feeling hungry ALL the time, right? That constant gnawing sensation that makes you miserable and eventually gives up on your health goals completely.
Here’s where the low carb diet really shines compared to other approaches. Studies consistently show that when people cut carbs and increase their protein and fat intake, they experience an automatic reduction in appetite without having to white-knuckle their way through cravings.
Why Low Carb Diets Crush Hunger So Effectively
Multiple research studies published in peer-reviewed journals demonstrate that carbohydrate restriction leads to eating far fewer calories naturally – without the conscious effort of counting every single bite. This happens because:
- Stable blood sugar levels – Without the constant glucose roller coaster from high-carb meals, you avoid the energy crashes that trigger intense hunger signals
- Increased satiety hormones – Higher protein and fat intake boosts hormones like peptide YY and CCK that signal fullness to your brain
- Reduced ghrelin production – The “hunger hormone” ghrelin decreases significantly on low carb eating patterns
- Better leptin sensitivity – Your body becomes more responsive to leptin, the satiety hormone that tells you when you’ve had enough
According to Healthline’s comprehensive review of low carb research, this appetite reduction is one of the most consistent findings across dozens of studies. People naturally consume fewer calories without feeling deprived or fighting constant cravings.
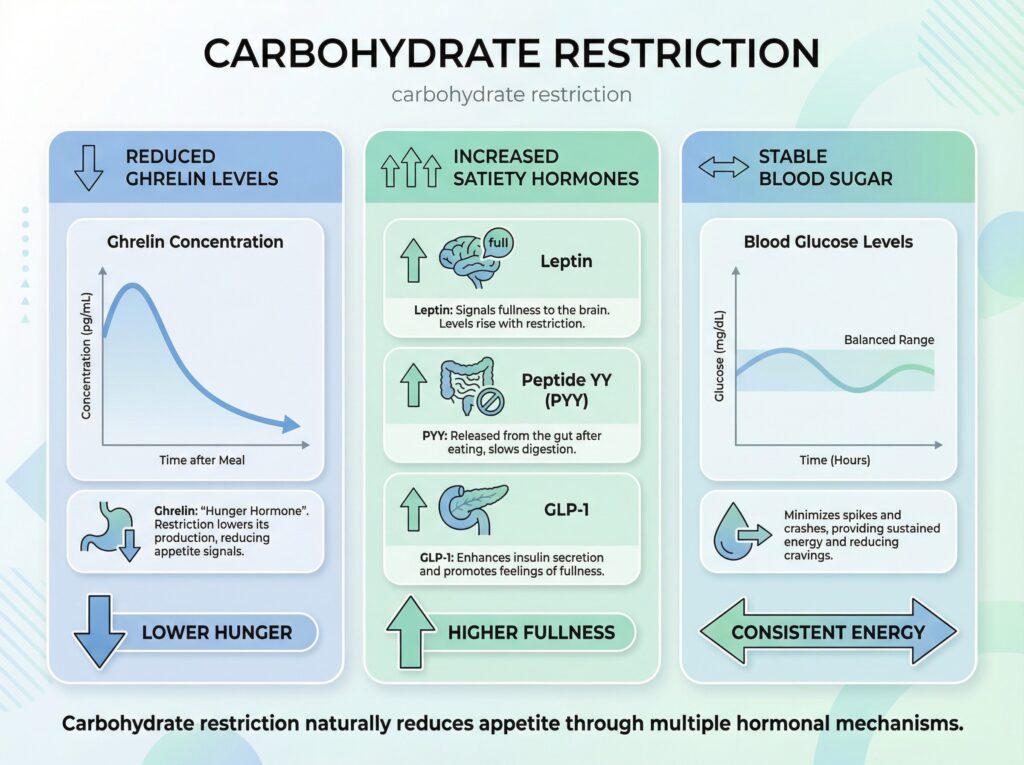
Image Description: Infographic showing hormone changes with carbohydrate restriction – reduced ghrelin, increased satiety hormones, stable blood sugar graph
Alt Text: carbohydrate restriction
Caption: Carbohydrate restriction naturally reduces appetite through multiple hormonal mechanisms
Benefit Two: Accelerated Weight Loss That Actually Lasts
Okay, this is probably the benefit that brings most people to the low carb diet in the first place – and the research backing it up is pretty solid.
Early studies on low carbohydrate eating reported greater weight loss compared to traditional low-fat diets, and more recent research continues to show advantages, particularly in the short to medium term.
The Science Behind Low Carb Weight Loss
When you slash your carb intake significantly, several fat-burning mechanisms kick into gear simultaneously:
- Lower insulin levels – Reduced carb intake dramatically decreases insulin secretion, and since insulin is essentially your body’s fat-storage hormone, lower levels mean your body can actually access and burn stored fat more easily
- Water weight loss – Your body stores carbs as glycogen along with water, so initial weight loss happens quickly as glycogen stores deplete
- Increased fat oxidation – Your metabolism shifts to preferentially burn fat for fuel once carb availability drops
- Metabolic advantage – Some researchers suggest low carb diets may provide a small metabolic advantage through increased energy expenditure
A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine found that participants following a low-carbohydrate plant-based diet achieved body weight reductions of about 4 kilograms – similar to results reported for Atkins diet-style approaches.
What’s particularly impressive is that many people maintain their weight loss better on low carb eating compared to traditional calorie-restricted diets, likely because the appetite suppression makes it easier to sustain the approach long-term.
Benefit Three: Revolutionary Blood Sugar And Insulin Control
This benefit is absolutely HUGE, especially if you’re dealing with prediabetes, Type 2 diabetes, or metabolic syndrome. The low carb diet has been shown to be incredibly effective for managing blood glucose and insulin levels.
How Low Carb Eating Transforms Glucose Metabolism
When you eat carbohydrates, they break down into glucose which enters your bloodstream, triggering insulin release from your pancreas. The more carbs you eat, the more insulin your body needs to produce to handle the glucose load. Over time, this can lead to insulin resistance – where your cells stop responding properly to insulin signals.
Research proves that cutting carbs lowers both blood sugar and insulin levels drastically. According to studies reviewed by Healthline, some people with diabetes who begin a low carb diet may need to reduce their insulin dosage by 50% almost immediately due to the dramatic improvement in blood sugar control.
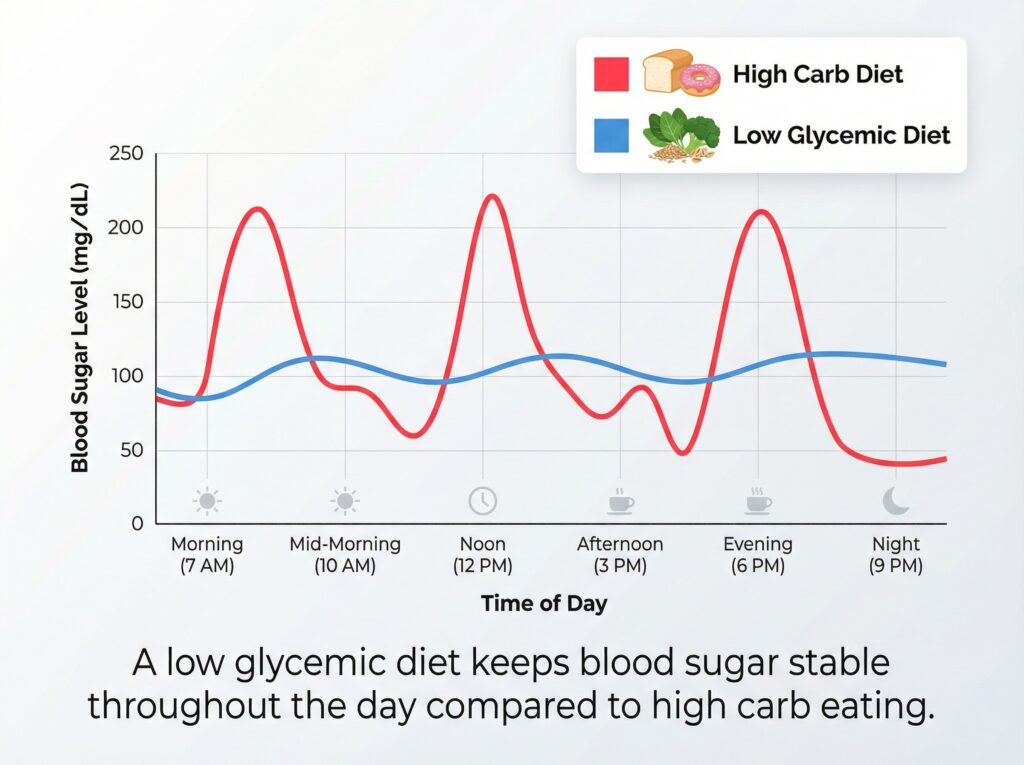
Long-Term Metabolic Health Improvements
A comprehensive review published in the journal examining low carbohydrate diet benefits found that carbohydrate restriction offers particular advantages in reducing diabetic medication needs while improving glycemic control.
For people with Type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing it, adopting a low carb diet under medical supervision can potentially:
- Reduce or eliminate the need for diabetes medications
- Lower HbA1c levels significantly over 3-6 months
- Improve insulin sensitivity throughout the body
- Reduce risk of diabetic complications like neuropathy and retinopathy
This makes low carb eating one of the most powerful dietary interventions available for metabolic health improvement.
Benefit Four: Significant Improvements In Heart Health Markers
Now this one might surprise you because for years we were told that eating more fat – especially saturated fat – would destroy our hearts, right? Well, the research on low carb diet effects on cardiovascular health tells a much more nuanced and often positive story.
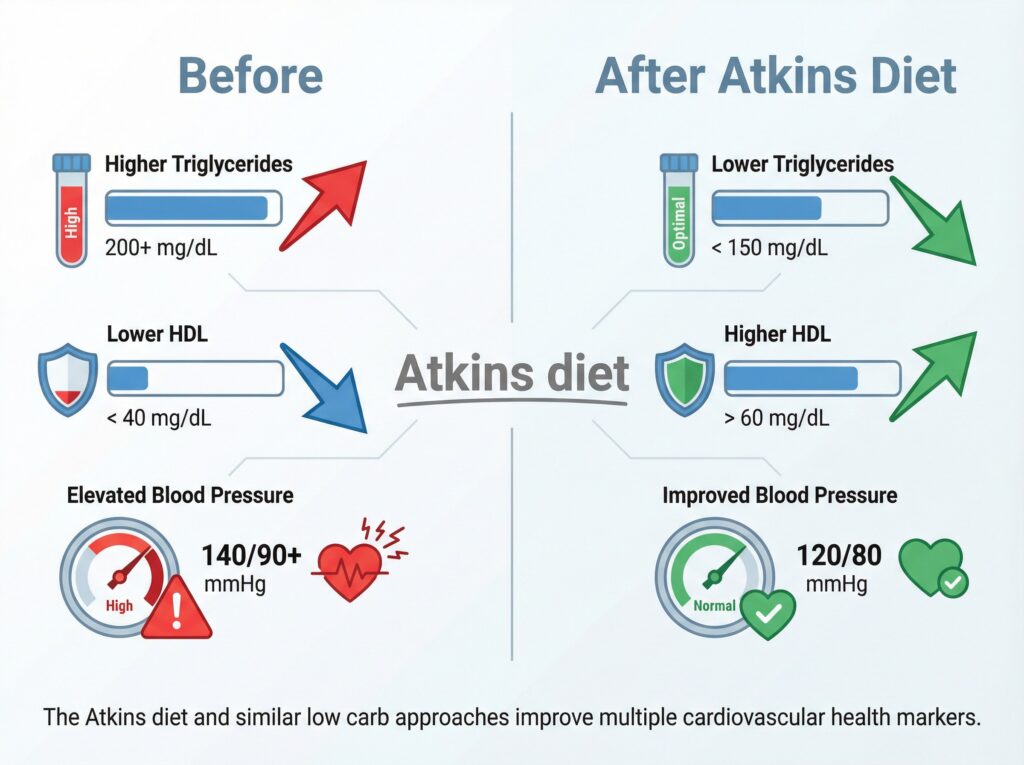
Triglyceride Reduction – A Major Win
One of the most consistent findings across low carb research is the dramatic reduction in triglycerides – fat molecules in your blood that are a major risk factor for heart disease.
Studies show that carbohydrate restriction can reduce triglyceride levels by 30-50% or more, which is pretty remarkable. High triglycerides are strongly associated with increased heart disease risk, so bringing them down significantly improves your cardiovascular health profile.
HDL Cholesterol Increases
The low carb diet tends to increase HDL cholesterol – often called the “good” cholesterol because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. Higher HDL levels are associated with reduced heart disease risk.
Research published in JAMA Internal Medicine demonstrated that even plant-based low carb approaches resulted in improved lipid profiles with significant reductions in LDL cholesterol and better cholesterol ratios.
Blood Pressure Reduction
Elevated blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. The good news? Low carb diets are an effective way to lower blood pressure naturally.
According to research compiled by Healthline, cutting carbs leads to a significant reduction in blood pressure, which should reduce your risk of these serious diseases and help you live longer.
Benefit Five: Enhanced Mental Clarity And Cognitive Function
If you’ve ever experienced that afternoon brain fog after a carb-heavy lunch, you already know firsthand how dramatically carbohydrates can affect your mental performance. The low carb diet offers some seriously impressive cognitive benefits that go beyond just avoiding the dreaded “food coma.”
Stable Energy Equals Better Brain Function
When you consume a lot of carbs, you’re basically loading your body with sugars that cause blood glucose levels to spike and crash repeatedly throughout the day. Your brain has difficulty managing what it needs to stay focused and awake when energy levels are constantly fluctuating like a roller coaster.
On a low carb diet, your blood sugar stays much more stable, providing your brain with consistent fuel without the crashes. Many people report:
- Improved focus and concentration that lasts all day
- Better memory retention and recall
- Enhanced mental clarity without brain fog
- More consistent energy without needing caffeine hits
Ketones As Premium Brain Fuel
When you restrict carbs enough to enter mild ketosis, your body produces ketone bodies that serve as an alternative fuel source for your brain. Some research suggests ketones may actually be a more efficient energy source for brain cells compared to glucose.
According to MedicineNet’s review of low carb benefits, studies report that low glycemic diet approaches may even be beneficial in preventing attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in youngsters because lower sugar consumption helps control the body’s energy levels and boosts the brain’s capacity to focus.
Benefit Six: Reduced Inflammation Throughout Your Body
Chronic inflammation is at the root of so many modern health problems – from arthritis and autoimmune conditions to heart disease and even cancer. The low carb diet has shown impressive anti-inflammatory effects that can improve overall health in multiple ways.
How Carbohydrate Restriction Fights Inflammation
When you eat a lot of refined carbohydrates and sugars, it triggers inflammatory pathways in your body. High blood sugar and insulin levels promote the production of pro-inflammatory molecules called cytokines.
By adopting carbohydrate restriction, you:
- Lower chronic insulin elevation – High insulin levels contribute to systemic inflammation throughout the body
- Reduce oxidative stress – Lower glucose levels mean less oxidative damage to cells and tissues
- Decrease inflammatory markers – Studies show reductions in C-reactive protein and other inflammation markers
- Balance omega fatty acid ratios – Many low carb diets emphasize foods with better omega-3 to omega-6 ratios
Research indicates that the metabolic improvements from a low carb diet translate into measurable reductions in inflammatory markers that are associated with chronic disease risk.

Benefit Seven: Potential Longevity And Disease Prevention Benefits
While we need more long-term studies to fully understand the relationship between low carb diet adherence and lifespan, emerging research suggests several mechanisms through which carbohydrate restriction might support healthy aging and disease prevention.
Cellular Health And Autophagy
When you reduce carb intake significantly, it can trigger autophagy – your body’s cellular cleanup process where damaged cell components get recycled and removed. This process is thought to play a role in preventing various age-related diseases and promoting longevity.
Reduced Cancer Risk Factors
Some research suggests that low carb diet patterns may help reduce certain cancer risk factors. Since many cancer cells rely heavily on glucose for fuel, limiting carbohydrate availability while maintaining adequate protein and healthy fats might create a less favorable environment for cancer cell growth.
However, it’s important to note that more research is needed in this area, and diet is just one factor among many that influence cancer risk.
Metabolic Health As Foundation For Longevity
Perhaps the most compelling argument for the longevity benefits of a low carb diet is the comprehensive improvement in metabolic health markers. By improving:
- Insulin sensitivity and glucose control
- Cardiovascular health markers
- Body composition and healthy weight
- Inflammation levels throughout the body
You’re essentially addressing multiple risk factors for the leading causes of death in developed countries – heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and certain cancers.
A review in StatPearls notes that low-carbohydrate diets have been linked to lower cardiovascular disease risk and improved metabolic indicators when followed appropriately.
How To Implement A Low Carb Diet Safely And Effectively
So now that you understand these seven powerful benefits, you’re probably wondering how to actually implement a low carb diet in a healthy, sustainable way.
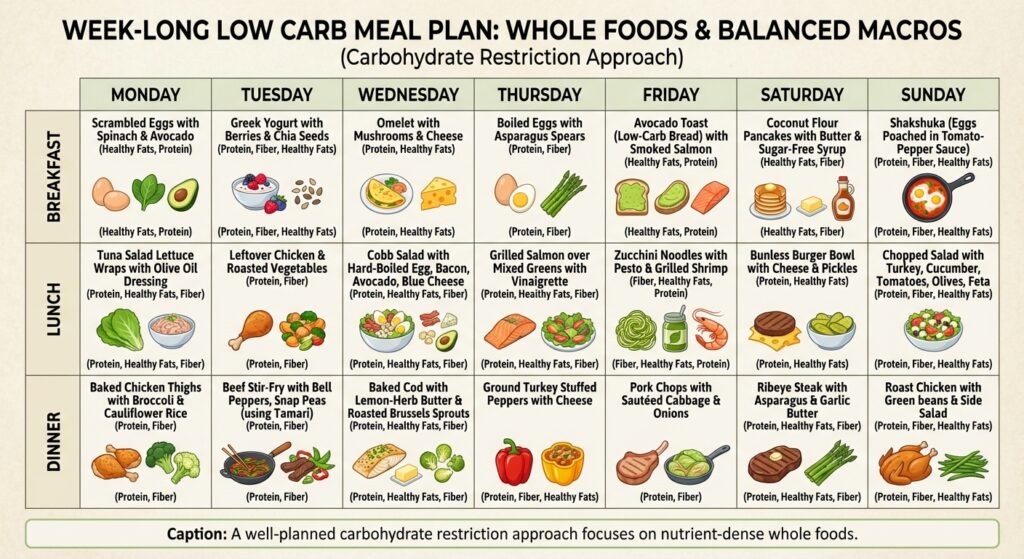
Start With Whole, Nutrient-Dense Foods
The key to getting all these benefits while avoiding potential pitfalls is focusing on nutrient-dense whole foods rather than just cutting carbs without considering overall nutrition quality. Your low carb diet should emphasize:
- Quality protein sources like fish, poultry, eggs, and grass-fed meats
- Healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish
- Non-starchy vegetables loaded with fiber, vitamins, and minerals
- Limited amounts of berries and other low-glycemic fruits
- Adequate hydration and electrolytes
Consider Different Low Carb Approaches
Not everyone needs to follow the same level of carbohydrate restriction. Different approaches include:
- Moderate low carb – Around 100-150 grams of carbs daily, suitable for active individuals
- Low carb – 50-100 grams daily, the sweet spot for many people
- Very low carb/ketogenic – Under 50 grams daily to achieve ketosis
- Low glycemic diet – Focusing on carbs with minimal blood sugar impact rather than strict limits
The Mayo Clinic recommends working with healthcare providers to determine the right approach based on your individual health status and goals.
Monitor Your Progress And Adjust
Give your body at least 2-4 weeks to adapt to carbohydrate restriction before judging results. Common adaptation symptoms like fatigue or headaches typically resolve as your metabolism shifts.
Track relevant markers including:
- Weight and body composition changes
- Energy levels throughout the day
- Blood sugar readings if diabetic
- How you feel mentally and physically
- Any changes in medications needed
Be Aware Of Potential Considerations
While the benefits can be substantial, it’s important to acknowledge that low carb diet approaches aren’t perfect for everyone. According to research, some people may experience:
- Initial adaptation symptoms like “keto flu”
- Potential nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned
- Social challenges when dining out
- Need for medication adjustments, especially for diabetes
Working with knowledgeable healthcare providers ensures you maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
The Bottom Line On Low Carb Diet Benefits For Health
The low carb diet represents a powerful nutritional approach backed by substantial scientific evidence for improving multiple aspects of health. From dramatic appetite reduction and effective weight loss to revolutionary improvements in blood sugar control, heart health markers, mental clarity, reduced inflammation, and potential longevity benefits – the advantages of carbohydrate restriction are hard to ignore.
What makes low carb eating particularly appealing is that many of these benefits happen relatively quickly – often within weeks of starting the approach. Unlike some dietary interventions that require months or years to show results, people frequently notice improved energy, reduced hunger, and better mental clarity within the first few weeks.
The key to success is implementing a low carb diet thoughtfully with emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods rather than simply eliminating carbs while loading up on processed meats and unhealthy fats. Whether you choose a moderate low glycemic diet approach or a more restrictive Atkins diet-style protocol, the focus should always be on improving overall nutrition quality while reducing carbohydrate intake.
For many people struggling with weight, blood sugar issues, metabolic syndrome, or simply wanting to optimize their health and energy levels, a well-formulated low carb diet offers a evidence-based solution worth serious consideration. As always, work with qualified healthcare providers to determine if this approach aligns with your individual health status, goals, and lifestyle needs.


